BREAST CANCER
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy among women globally. It remains the most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide, and has now surpassed lung cancer as the leading cause of global cancer in 2020, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases, representing 11.75% of all cases. It affects people of all ages and genders and has become a public health concern. Hence, it is necessary to spread awareness about breast cancer.
What is Breast Cancer??
Breast cancer is the cancer that originates in the breast. It occurs when cell in the breast mutate and grow uncontrollably and create a mass or lump in the breast. Mostly middle aged women 45-50 years old are affected. Rarely seen in males and children.
Breast cancer arise from-
- Glandular tissue- glands that form milk
- Fibrous tissue and fatty tissue
- The nipple
- Blood vessels and lymphatic vessels
Burden Of Breast Cancer
In India, in early 1990, cervical cancer was the leading site of cancer, followed by breast cancer. But now since 2000, breast cancer is the leading site of the cancer. India leads in mortality with 98,337 deaths in 2022. The incidence and mortality rate was high in younger females (less than 29). This number is going to increase by 2050. According to ICMR, there is variation in its incidence between rural and urban population with occurrence of 5 per 1 lakh cases in rural area as compared to 30 per 1 lakh cases in urban areas. This inequality is more pronounced in urban metro cities and northeastern regions of India.
Signs and Symptoms
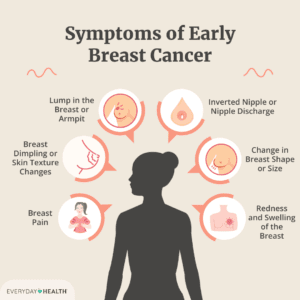 Any lump or swelling in the breast or armpit
Any lump or swelling in the breast or armpit- Thickening or swelling of part of the breast
- Irritation or dimpling of breast skin
- Redness or flaky skin in the nipple areas or the breast
- Pulling in of the nipple or pain in nipple areas
- Nipple discharge other than breast milk
- Any change in the size and shape of the breast
- Pain at any site in the breast.
These symptoms can also be a benign condition of the breast. So it is necessary to consult your doctor before giving the name of cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors for Breast Cancer
- Alcohol intake- Moderate alcohol intake (15-30g/day) has been linked to an approx 30-50% increased risk of breast cancer.
- Obesity- In premenopausal women, an inverse association between obesity and breast cancer risk has been reported. But in postmenopausal women, obesity is consistently associated with a higher incidence of breast cancer. A study reported that postmenopausal breast cancer risk was positively associated with each 5kg/m2 increase in BMI. Adipose (fatty tissue) in obese individuals upregulates estrogen hormone formation. This excess of estrogen exposure causes mammary cell proliferation and genetic instability.
- Sedentary lifestyle- It increases the breast cancer risk independently by 10-15%, as it elevates circulatory estrogen, insulin, and chronic inflammation. Thus, it promotes obesity, mammary cell proliferation, and DNA damage.
- Reproductive history- A woman’s reproductive history reflects her lifetime exposure to sex hormones (esp estrogen). These factors are:
early menarche <12 years of age
late menopause >55 years of age
Nulliparity
Hormone therapy after menopause
No history of breastfeeding
Late age at first pregnancy
These all factors lead to increased exposure to ovarian hormones (esp estrogen), which causes cell growth. Infertility treatment, IVF, or hormone intake like OCPs, IUDs, vaginal implants, do not cause breast cancer.
5. Age: Risk increases with age. Mostly diagnosed after 50 years of age.
6. Genetic Mutation: Mutations to certain genes, like BRCA1 and BRCA2, increase the risk of breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
7. Breast density: It is directly proportional to the breast cancer risk.
8. Past History: History of any breast cancer, non-cancerous breast disease, like atypical ductal hyperplasia
9. Family history: History of breast cancer in first-degree relatives, like mother, sister, or daughter.
10. Radiation Exposure.
Types of Breast Cancer
- Ductal Carcinoma in situ- It is a non-invasive, asymptomatic, stage 0 of breast cancer. Detected by screening, highly treatable.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma- It begins in the milk duct and has spread into the surrounding tissue.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma- It begins in the milk glands and may or may not involve the surrounding breast tissues.
- Triple negative breast cancer- It is a rare but aggressive type of breast cancer that lacks the hormone receptors. It impacts the treatment options.
- Inflammatory breast cancer- It is a fast-growing cancer, affecting the skin around the breast. It is also rare but aggressive.
- Metastatic breast cancer- It is a stage 4 cancer. Disease has spread from one site to other areas of the body, mainly the bones, liver, lungs, and brain.
- Other types- Paget’s disease of the breast, Angiosarcoma, phyllodes tumour.
Staging of Breast Cancer
Stage 0: Ductal carcinoma in situ, cancer cells confined to milk ducts. They have not invaded the surrounding tissue.
Stage 1: Early invasive stage, where cancer cells have invaded the breast tissue.
Stage 2: Invasive stage, a stage where the size of the tumour is large, may or may not involve lymph nodes, but is confined to the breast only.
Stage 3: Locally advanced, here the tumour size is very large and extensively involves the lymph nodes.
Stage 4: Metastatic, at this stage, cancer spreads to distant parts of the body, like bones, liver, lungs, and brain. Etc.
Screening and Diagnosis
Many cancers are asymptomatic. Hence, routine screening is necessary to treat them effectively at an early stage. Breast cancer, cervical cancer are such types of cancer, can be detected and treated early. Screening guidelines are advised for them, and mammography is the screening tool.
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (ACOG), the guidelines for screening are:
Initiation age: Offer screening at the age of 40
Initiate screening at the age of 40-49 after counselling, if the patient desires
Not recommended after 50 years of age, if they have not initiated screening
Screening interval: Annually or Biannually.
Diagnosis- Its diagnosis begins with the clinical examination and the history of symptoms. Imaging and biopsy confirm the diagnosis.
Tools for diagnosis-
- Mammogram- X-ray of breast tissue. Most commonly used tool. Avoid in pregnancy.
- Breast USG-To differentiate between the lump or fluid-filled cavity
- Breast MRI- Used to look at the areas of the breast involved in cancer
- Biopsy. A piece of tissue is cut out for testing in a laboratory under the microscope.
- Other tests.- Bone scan, CT scan, and PET scan to see the staging of cancer.
Treatment for Breast Cancer
Treatment depends on many factors, like age, cancer, staging of cancer, and associated comorbidities.
- Breast cancer surgery- Removal of the lump (lumpectomy) or breast (mastectomy). Either of them can be done depending on the size of the tumour.
- Chemotherapy or hormonal therapy- They are given before the surgery to reduce the size of the tumour. But if given after the surgery, then it is to kill the remaining cancer cells to lower the risk of relapse.
- Radiation therapy- Most often used after the surgery to kill the cancer cells left after the surgery.
- Targeted therapy- A therapy where medicine targets specific types of chemicals or receptors in cancer cells, like HER-2
- Immunotherapy- A therapy that helps the immune system to kill the cancer cells
- Palliative care- It is an approach that aims to improve the quality of life for patients and their families facing life‑threatening illness through early identification, assessment, and treatment of pain and other problems.
Prevention of cancer
Breast cancer cannot be completely prevented, but the overall risk can be reduced by modifying our lifestyles, appropriate screenings in high-risk women.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity, breast density a risk factors for breast cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding obesity prevents breast cancer.
- Regular exercise: Exercise helps in decreasing risk of breast cancer as it decreases the risk of breast cancer by changing the estrogen, insulin, and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). A sedentary lifestyle is associated with weight gain and an increased risk of breast cancer. Therefore, physical activity should be recommended to women who are at an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Smoking cessation: Smoking is an important risk factor for breast cancer. Both active and passive smokers are at an increased risk of breast cancer. Therefore, smoking is another behaviour that can be altered. It is recommended that women stop smoking to decrease the risk of breast cancer and other cancers.
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Breastfeeding: It decreases the risk of breast cancer as it decreases the number of menstrual cycles in a lifetime and thus decreases the exposure to estrogen.
- Know your family history: If your family history is positive, then go for regular screening for breast cancer.
While no one can erase their breast cancer risk, everyday choices truly matter. By staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol, eating a nutrient‑rich diet, and keeping up with age‑appropriate screening, you give yourself the best possible chance of early detection and risk reduction. Remember, the goal is not perfection but consistent, sustainable habits—and partnering with your healthcare provider to understand your personal risk and create a plan that works for you.
References
Pingback: Obesity, a health burden